RAVEN
Risk Analysis Virtual ENvironment
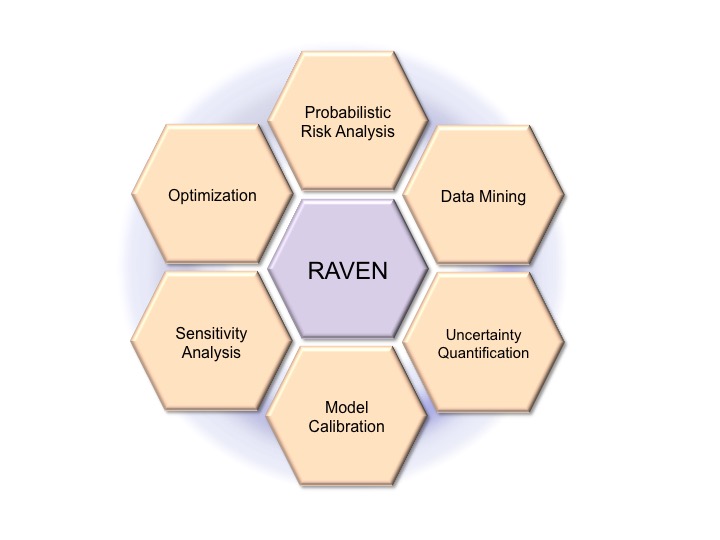
RAVEN (https://github.com/idaholab/raven) is an open source software platform that facilitates and enhances a variety of model exploration, risk analyses and design optimizations for nuclear reactors, energy grids and other complex systems.
At the most basic level, RAVEN samples the response of a complex system according to parameter alterations provided by the user. The user relies on third-party data to model the complex system under analysis, and RAVEN accesses the model data through application programming interfaces or input/output files. RAVEN then employs a variety of statistical techniques (e.g., Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube sampling, or reliability surface search) or machine learning to analyze how parameter alterations affect the system model. Machine learning can be particularly useful to reduce the computational burden of these analyses by creating a simpler digital representation of the system being modeled. In addition to improving the interface between a simulation model and its input data, RAVEN also enables analysts to link simulation models together, allowing the output of one simulation model to be used as the input for another simulation model. RAVEN also makes it easy to run customizable analysis workflows using a variety of sampling and optimization strategies.
The data generated by the sampling process is analyzed using classical statistical and more advanced data mining approaches. RAVEN also manages the parallel dispatching (i.e., both on desktop/workstation and large High Performance Computing machines) of the software representing the physical model. RAVEN heavily relies on artificial intelligence algorithms to construct surrogate models of complex physical systems in order to perform uncertainty quantification, reliability analysis (limit state surface) and parametric studies.


Development
The development of RAVEN started in 2012 to satisfy the need to provide a modern risk evaluation framework. RAVEN’s principal assignment is to provide the necessary software and algorithms in order to employ the concept developed by the Risk Informed Safety Margin Characterization (RISMC) path-way (now called Risk-Informed System Analysis – RISA). RISMC/RISA is one of the pathways defined within the Light Water Reactor Sustainability (LWRS) program. In the RISMC/RISA approach, the goal is not just specifically identifying the frequency of an event potentially leading to a system failure, but also to analyze the “distance” and the drivers toward the happening of key safety-related events. This approach may be used in identifying and increasing the safety margins related to those events. A safety margin is a numerical value quantifying the probability that a safety metric (e.g. as peak pressure in a pipe) is exceeded under certain conditions. The initial development of RAVEN has been focused on providing dynamic risk assessment capability to system codes (RELAP7, RELAP5, etc). Most of the capabilities have been agnostically implemented.
Program Credits
As already mentioned, RAVEN development has been initiated within the RISMC path-way; during the past years, other projects have contributed to its development, among which, the main contributors are: